Interest Rates Cut
 Yesterday, the Federal Reserve announced the most considerable rate cut in over four years!
Yesterday, the Federal Reserve announced the most considerable rate cut in over four years!
This marks a significant adjustment in the market, potentially offering buyers the opportunity to benefit from reduced monthly mortgage payments and increased affordability.
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate cut of 50 basis points on September 18, 2024, is expected to significantly impact the U.S. economy in the last quarter of 2024.
Here’s how:
Boost to Consumer Spending
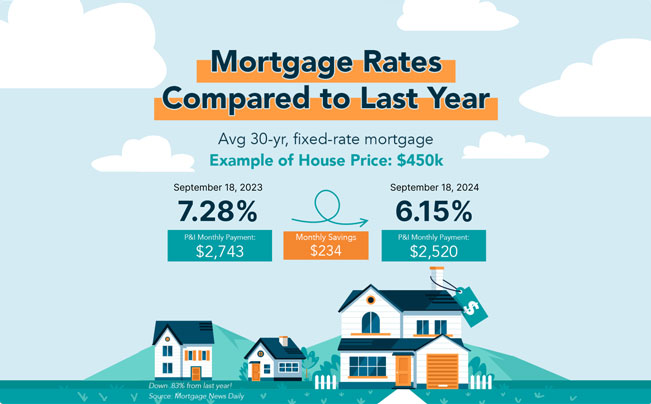
Lower interest rates reduce consumers’ borrowing costs, which could stimulate spending on big-ticket items like homes and cars. Mortgage rates are expected to drop, encouraging more activity in the housing market and relieving current homeowners looking to refinance their loans.
Business Investments
With lower borrowing costs, businesses may find loans for expansion or other investments more attractive. This could lead to a surge in corporate activities, particularly in sectors like private equity, where firms are expected to engage in dividend recapitalizations and other transactions to enhance returns.
Labor Market Stabilization
The Fed’s rate cut is intended to mitigate risks to the labor market, which has shown signs of weakening despite low unemployment rates. By reducing borrowing costs, the Fed hopes to prevent further deterioration in job creation and support continued employment growth (politico).
Inflation Management
The rate cut is part of a broader effort to encourage inflation to trend downward toward the Fed’s 2% target. By easing monetary policy, the Fed aims to balance controlling inflation with supporting economic growth, thus striving for a “soft landing”—slowing inflation without triggering a recession.
While the rate cut will likely provide short-term relief and boost economic activity, there are still concerns about potential future risks, especially in the labor market. The long-term success will depend on how effectively inflation is managed and whether businesses and consumers respond positively to the lower rates.
Prediction
The predicted home price appreciation rate for the first quarter of 2025 is expected to slow compared to previous years but will still show positive growth. Following the Federal Reserve’s interest rate cut in September 2024, home prices are forecasted to increase by around 3.2% for 2025, down from the anticipated 4.3% in 2024. This moderation in growth reflects easing mortgage rates and a gradual increase in housing inventory, as sellers previously holding back have begun listing their homes (FannieMae).
Although mortgage rates are expected to decline into 2025, affordability challenges and inventory growth will likely temper the pace of price increases, especially compared to the more robust gains seen in 2023. This means that while home prices will continue to rise, they will do so at a slower rate, which could provide some relief to prospective buyers.